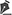A 32-year-old male patient was hospitalized for worsening symptoms of odynophagia, fever, and malaise. Laboratory tests confirmed acute myeloid leukemia. The patient then presented with severe hypoxemic respiratory failure caused by influenza B virus and rhinovirus infection, requiring mechanical ventilation and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. The patient was then started on treatment with all-trans-retinoic acid, hydroxyurea, dexamethasone, and broad-spectrum antibiotics. Antifungal therapy was added because of persistent fever, worsening radiological findings, and galactomannan-positive BAL fluid. One week later, a follow-up chest X-ray showed an air crescent sign within a parenchymal consolidation. A CT scan of the chest confirmed cavitary lesions with solid content and an air component around them, characterizing the air crescent sign, which is consistent with angioinvasive aspergillosis in patients undergoing treatment for and in the recovery phase of hematologic malignancies, as a result of increased granulocytic activity. The differential diagnosis in this setting includes other invasive fungal diseases, pulmonary infarction, necrotizing pneumonia, and lung abscess.

Aspergillus infection is a life-threatening condition in immunosuppressed patients.(1) Aside from biological testing, CT is particularly useful because the finding of a halo sign together with a positive galactomannan test can allow early diagnosis and treatment. The air crescent sign is a finding that suggests good therapeutic response in these patients.(2,3)
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS SSF: conceptualization; investigation; and drafting and reviewing of the manuscript. APZ and RDG: conceptualization; investigation; and reviewing of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST None declared.
REFERENCES 1.Sales Mda P. Chapter 5--Aspergillosis: from diagnosis to treatment. J Bras Pneumol. 2009;35(12):1238-1244. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1806-37132009001200012
2.Curtis AM, Smith GJ, Ravin CE. Air crescent sign of invasive aspergillosis. Radiology. 1979;133(1):17-21. https://doi.org/10.1148/133.1.17
3.Chong WH, Ibrahim A, Saha BK. The evolution of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis on chest imaging in response to antifungal therapy. BMJ Case Rep. 2021;14(3):e242576. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2021-242576